Steps of Meiosis and Mitosis
Online Biology Dictionary
|
|
EUGENE M. MCCARTHY, PHD GENETICS
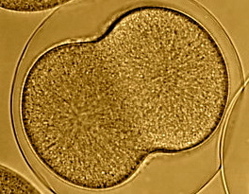 During the final steps of meiosis and mitosis an indentation called the "cleavage furrow" forms, ringing the equator of the dividing cell.
During the final steps of meiosis and mitosis an indentation called the "cleavage furrow" forms, ringing the equator of the dividing cell.
The steps of meiosis and mitosis in order:
| Mitosis | Meiosis I | Meiosis II |
Prophase | Prophase I | Prophase II |
Metaphase | Metaphase I | Metaphase II |
Anaphase | Anaphase I | Anaphase II |
Telophase | Telophase I | Telophase II |
|
An additional stage of mitosis, prometaphase, is sometimes distinguished. Read more about prometaphase >> | ||
| To help your memory: You can remember the first letters of each of the stages of meiosis and mitosis in order by remembering any one of these sentences: "Perhaps my Aunt Tillie." OR "Passed my anatomy test!" OR "Peter made a tart." Take your pick! |
|
A silly mneumonic poem: Mitosis happens everywhere, even in my toe, Meiosis only happens in my OH! |
|
Eduard Adolf Strasburger (1844-1912)
Three of the steps of meiosis and mitosis, prophase, metaphase, and anaphase, were coined by the Polish-German botanist Eduard Strasburger (Strasburger 1884, pp. 250 and 260), who together with Walther Flemming (1843-1905) and Edouard van Beneden (1846-1910) was the first to describe the process of chromosome distribution during cell division (telophase was only later given a distinct name). In Strasburger's description of the steps, metaphase continued until the daughter chromosomes were entirely separate from each other, whereas today it is usually regarded as ending as soon as the kinetochores begin to move towards the poles. Ana is a Greek word meaning, among other things, back, which to Strasburger referred to the chromosomes moving back into compacted nuclei. Strasburger also originated the terms cytoplasm and nucleoplasm, and was the first to accurately describe the embryo sac and to demonstrate double fertilization in angiosperms. Cited reference: Strasburger, E. 1884. Die Controversen der indirecten Kerntheilung. Archiv für mikroskopische Anatomie 23:246-304. |
Meiosis Stages © Macroevolution.net - All rights reserved |