Discovery of Reverse Transcriptase
Online Biology Dictionary
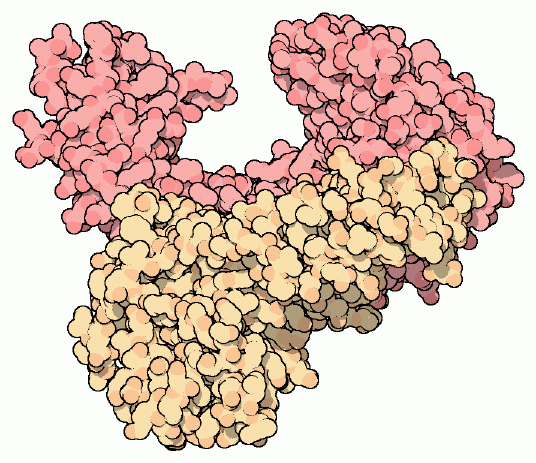 Reverse transcriptase (RT) of AIDS virus HIV-1
Reverse transcriptase (RT) of AIDS virus HIV-1
EUGENE M. MCCARTHY, PHD
|
|

|
| David Baltimore |

|
| Howard Temin |

|
| Renato Delbucco |
For their discovery of the viral enzyme reverse transcriptase (RT), Howard Temin, David Baltimore, and Renato Dulbecco shared the 1975 Nobel Prize for Physiology or Medicine. Temin and Baltimore discovered this enzyme, also known as RNA-dependent DNA polymerase, at the same time, but independently of each other. Dulbecco took no direct part in their experiments, but it was he who had taught them the methods they used to make their discovery.
RT is an enzyme produced by retroviruses, which are RNA viruses that make DNA copies of themselves and then insert those copies into host chromosomes. It plays an essential role in the reproduction of these molecular parasites. Well-known examples of retroviruses that can infect human beings are the agents of such diseases as AIDS or herpes.
Some retroviruses — oncoviruses — cause normal cells to become cancerous. Dulbecco's lab was the first to demonstrate this fact. They showed that the infection of normal cells with oncoviruses leads to the insertion of viral genes into host-cell chromosomes, which in turn can cause the cell to transition to a state of uncontrolled growth that gives rise to a malignant tumor (cancer). Oncoviruses are the cause of some forms of human cancer. However, in order to replicate a retrovirus must make a DNA copy of itself and then insert that copy into a host chromosome.
More about reverse transcriptase >>